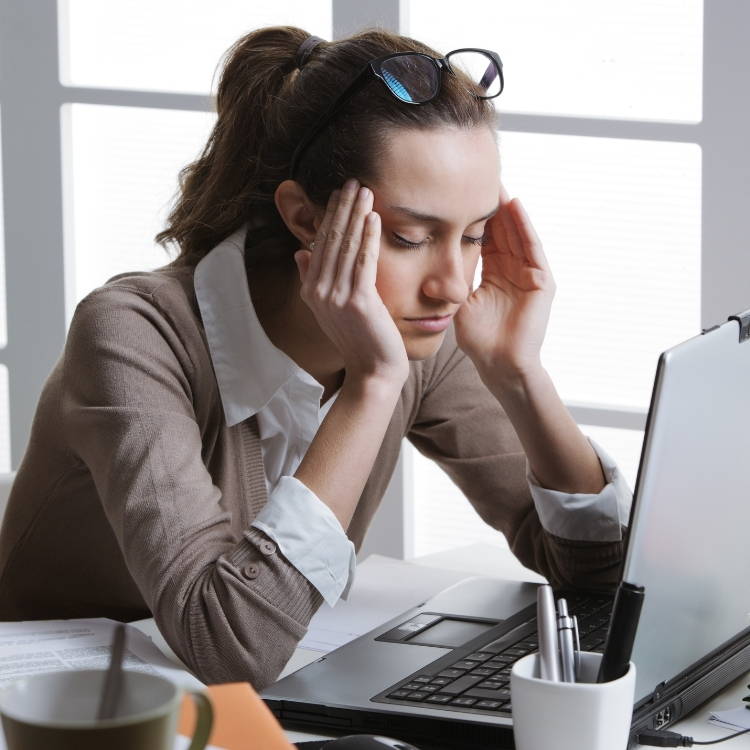
You See the Damage Orofacial Muscle Dysfunctions Can Cause Every Day
Do Your Patients Have Any of these symptoms?
Chronic digestive discomforts (aerophagia): bloating, burping, flatulence, abdominal distension, some forms of IBS and acid reflux.
Chronic headaches
Scar tissue in the oral-facial region that is causing discomfort or strained range of motion
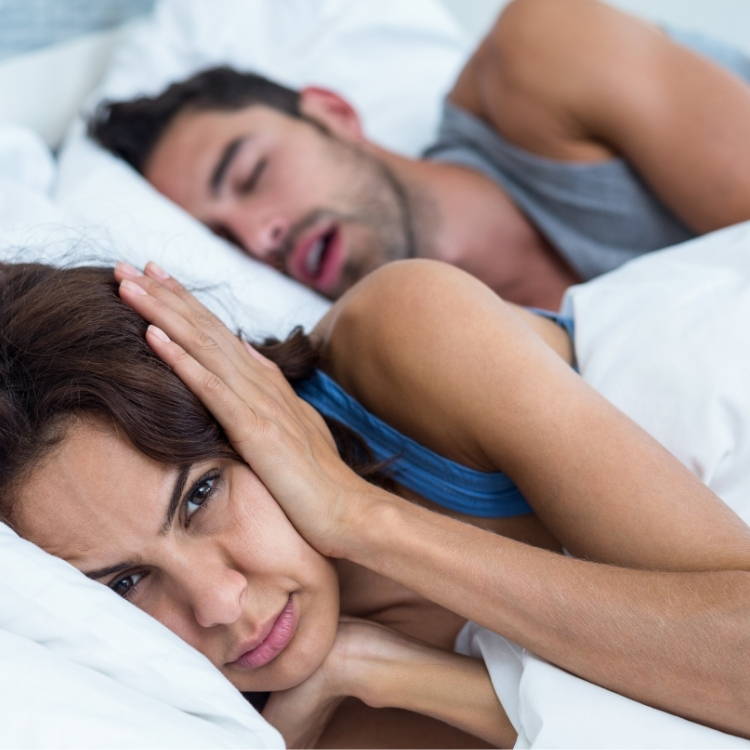
Sleep disordered breathing (snoring or apnea diagnosis)
Overnight dry mouth with or without medications
Memory troubles, brain fog, decreased productivity.
Mouth breathing or lips resting open.
Breathing difficulties, asthma
Non-nutritrive daily oral habit.
Unexplained facial, jaw, neck or upper back pain
Slow to heal
Asymmetrical facial features
Sinus infections
These are all side-effects of detrimental habits which can be improved
Oral-Facial Advantage Program Description
It begins by eliminating any noxious oral habits that can be detrimental to the treatment and long term success of the program.
Once eliminated, we train a neutral oral resting posture which tones and/or relaxes the muscles and tissues of the tongue, throat, jaw, face, head, and neck.
This sets the patient up to have the correct toning and positioning for the deglutition program. They begin with the swallowing of water, then soft, medium, hard, and mixed foods. From snacks to main meals, until the corrected practice is naturally a part of their daily life.
Throughout the program their sleep disordered breathing pattern is being reset. Their upper airway is being toned from all angles, they have a new beneficial oral resting posture, and the re-trained swallow pattern is being repeated throughout the night. Locking in muscle memory for long-term oral-facial comfort.
The Oral-Facial Advantage Program re-trains deeply ingrained detrimental oral and facial habits with new beneficial ones. The Orofacial Myologist uses easy to-do, scientifically designed muscle/tissue exercises, personalized to the individual's orofacial disorder.
Let us work together, igniting a myriad of health advantages in the short and long-term.
Some Of The Orofacial Dysfunctions We Re-Train

Upper Chest Breathing
Spinal Strain
Mouth Breathing
Postural Problems
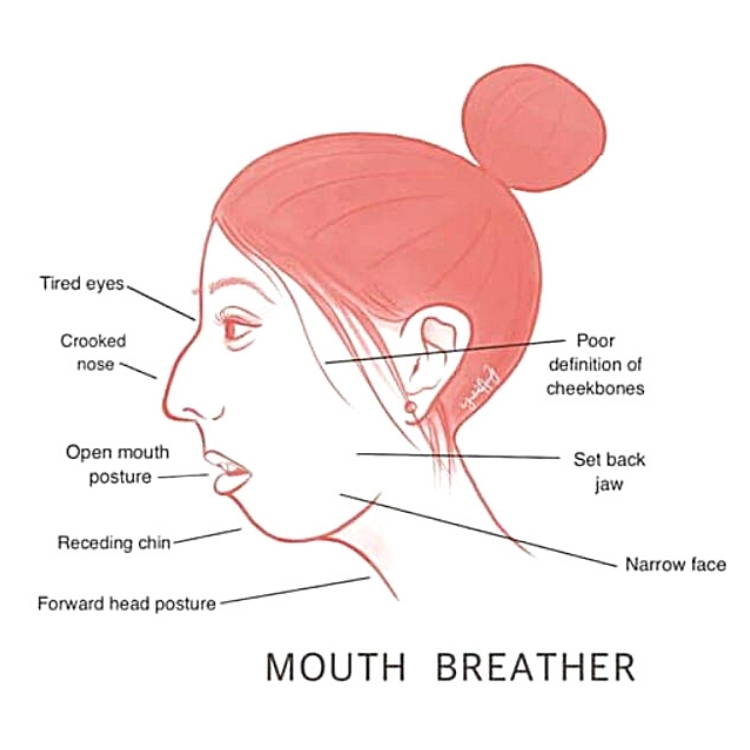

Mouth Breathing
Snoring & Apnea
Mouth Breathing
Causes Long Face Syndrome11,16,19,23
Crooked Teeth
Narrow Jaw & Face
Poorly Defined Cheekbones
Jaw Set Back/Malocclusion
Caries/Perio/Xerostomia
Dries out our bodies and mouths 42% more than nasal breathing, contributes to dehydration22
Causes cavities and gum disease23
Sleep Disordered Breathing further exasperates Xerostomia12
"If mouth breathing is treated early, its negative effects on facial and dental development, along with medical and social problems associated with it, can be reduced or averted"16


Damaging Oral Resting Postures
"Even without oral airflow, when the mouth is open, scientists have shown that the upper airway is more likely to collapse. Conversely, nose breathing with correct tongue resting posture during sleep improves airway diameter, engages the diaphragm56 and increases lung volume. This causes the airway wall to stiffen and helps the upper airways to stay open."57
The tongue from the tip to the posterior needs to be toned to rest in the palate. Most tongues are untrained/untoned, which can cause snoring and apnea.35,36
Narrow Jaw & Palate, Crooked/Crowded Teeth
Soft Foods = Shrinking Jaws
Stanford University Article, Shrinking Jaws:36
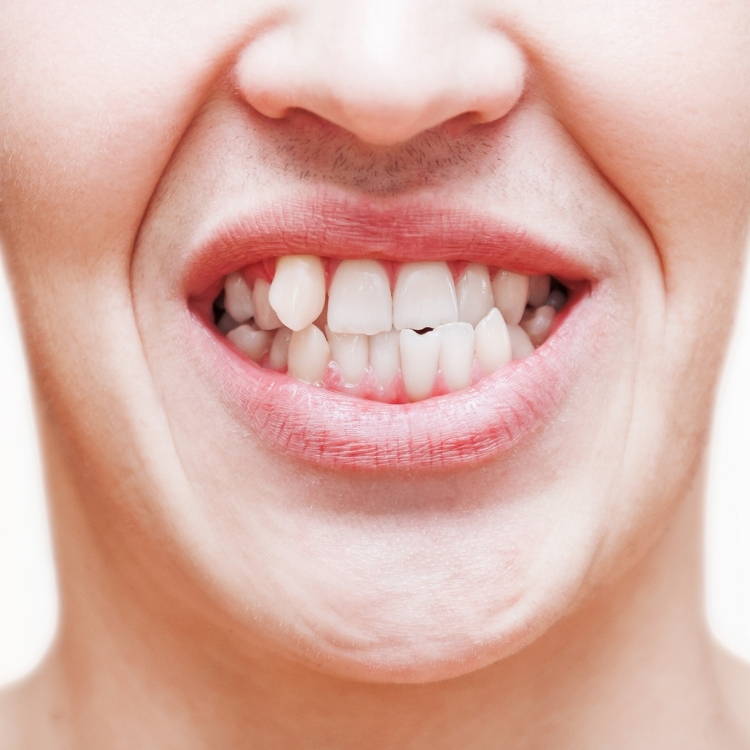

Tongue Thrust During Atypical Swallowing
Even an untoned tongue is made of 8 strong muscles. The tongue resting incorrectly puts considerable pressure against oral structures. These structures don't have the strength to resist causing bone loss around the teeth and tooth mobility (one cause of periodontal disease).17,18,19
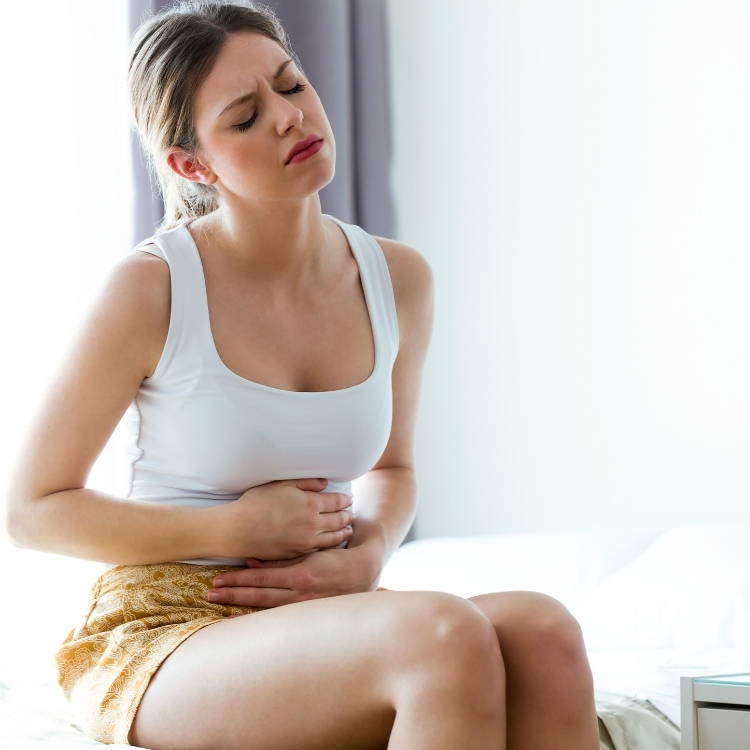
Aerophagia Definition: The swallowing of air, whether accidentally, or as an involuntary habit.52
Produces Uncomfortable Gastrointestinal Symptoms:34,49,50,51
Abdominal Distension
Bloating
Belching
Flatulence
Some Types of Acid Reflux & IBS


Sleep Disordered Breathing (Snoring/Apnea)12
Depression6
ADHD11,13,14,15
Memory Loss8,16
Mental Confusion16
High Blood Sugar Levels3
Deprives Body of Needed Oxygen Levels24
Linked to Fatty Liver Disease4
Decreased Growth Hormone Levels31,32,33
Asthma Symptoms & Increased Risk of Asthma Complications5
Abnormal Cholesterol2
Ankyloglossia (Tongue-Tied)
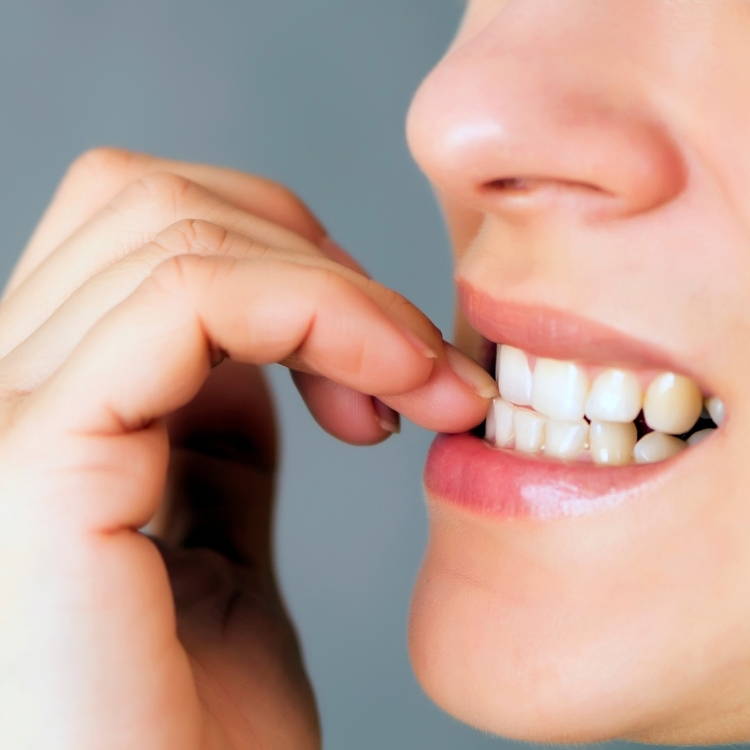


Repetitive Non-Nutritive Oral Habits
Habits: Sucking thumb, finger, lips, or biting nails, cheeks, tongue, hair...etc.
Open Bites, Malocclusion, Crooked Teeth38,39,41,45
Narrow Jaw41,43,44
Vaulted Palate43,44
Tonsil/Adenoid infections/swelling53
Long Face Syndrome39,41,42,43,45
Ortho Relapse19
Sleep Disordered Breathing12
Asymmetrical Face39,41,42,43,45
The Oral-Facial Advantage Program
Most programs last approximately 1 year.
Patients are seen weekly and assigned exercises that tone or relax the muscles in their head/neck region specific to their disorder.
You will be updated throughout their treatment progress.

At What Age Can Patients Begin Oral-Facial Muscle Therapy?
All ages.
The biggest impact can be made with children since their oral-facial structure and behavior is in a more flexible stage of growth. As adults, our muscles and tissues can be toned and relaxed where needed, making a large impact on how we age and the quality of life into our senior years. Make a difference in your health at any age.
Mature 3 to 4 year old mouth breathers can learn nasal breathing.
A mentally prepared 5 year old can begin the Oral Habit Elimination Program.
A 7 to 8 year old and up can start the Oral-Facial Advantage Program.
Who is Eligible for a Free Consult?
Everyone.
All ages can come in for a free consult.
It is a great opportunity for the patient's questions to be answered and to meet the Orofacial Myologist.
1Key, Josephine. “‘The core’: understanding it, and retraining its dysfunction.” Journal of bodywork and movement therapies 17, no. 4 (2013): 541-559.
2Gunduz C, et al "Obstructive sleep apnea independently predicts lipid levels: Data from the European Sleep Apnea Database" Respirology 2018; DOI: 10.1111/resp.13372.
3Jimmy Doumit, Bharati Prasad. "Sleep Apnea in Type 2 Diabetes" Diabetes Spectrum 2016 Feb; 29(1): 14-19.
4Omar A. Mesarwi, Rohit Loomba, Aul Malhotra. "Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Hypoxia, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease" ATS Journals 2018 Nov; V199, I7.
5Bharati Prasad, Sharmilee M. Nyenhuis, Ikuyo Imayama. "Asthma and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Overlap: What has the evidence taught us?" ATS Journals 2019 Dec;V201, I11.
6Ejaz, Shakir M et al. “Obstructive sleep apnea and depression: a review.” Innovations in clinical neuroscience vol. 8,8 (2011): 17-25.
7Djupesland PG, Chatkin JM, Qian W, Haight JS. Nitric oxide in the nasal airway: a new dimension in otorhinolaryngology. Am J Otolaryngol.2001 Jan; 22(1): 19-32.
8Lunn M, Craig T. Rhinitis and sleep. Sleep Med Rev. 2011 Oct;15(5):293-9
9Muliol J, Maurer M, Bousquet J. Sleep and allergic rhinitis. Journal Investigation Allergol Clinical Immunology. 2008;18(6):415-9.
10Ohki M, Usui N, Kanazawa H, Hara I, Kawano K. Relationship between oral breathing and nasal obstruction in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1996;523:228-30.
11Jefferson Y. Mouth breathing: adverse effects on facial growth, health, academics and behaviour. General dentist. 2010 Jan- Feb; 58 (1): 18-25.
12Fitzpatrick MF, McLean H, Urton AM, Tan A, O’Donnell D, Driver HS. Effect of nasal or oral breathing route on upper airway resistance during sleep. Eur Respir J. 2003 Nov;22(5):827-32.
13“ADHD and Sleep.” ADHD & Sleep Problems-National Sleep Foundation. National Sleep Foundation, 2017. Web. 11 Feb.2017. https://sleepfoundation.org/sleep-disorders-problems/adhd-and-sleep.
14Shur-Fen Gau S. Prevalence of sleep problems and their association with inattention/hyperactivity among children aged 6-15 in Taiwan.J Sleep Res. 2006 Dec;15(4):403-14.
15Borres MP. Allergic rhinitis: more than just a stuffy nose. Acta Paediatrica. 2009 Jul;98(7):1088-92)
16Pereira F, Motonaga S, Faria P, Matsumoto M, Trawitzki L, Lima S, Lima W. Myofunctional and Cephalometric Evaluation of Mouth Breathers. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2001. 67 (1): 43-49.
17Garliner D. Myofunctional Therapy. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1976. Print.(10-12)
18John E. Hall, Arthur C Guyton. Tongue posture and swallowing. Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology, 12th edition. 2010; 763-765.
19Paskay L. OMD Orofacial Myofunctional Disorders: Assessment, prevention and treatment. JAOS. 2012 march-april; 34-40.
20Okuro RT, Morcillo AM, Ribeiro MÂ, Sakano E, Conti PB, Ribeiro JD. Mouth breathing and forward head posture: effects on respiratory biomechanics and exercise capacity in children. J Bras Pneumol.2011 Jul-Aug; 37(4):471-9.
21Damaging Effects of Forward Head Posture.(2015, January 22). Retrieved from http://www.denvertechchiro.com/files/fhp_revised.pdf
22Svensson S, Olin AC, Hellgren J. Increased net water loss by oral compared to nasal expiration in healthy subjects. Rhinology. 2006 Mar;44(1):74-7. PMID: 16550955.
23Surtel A, Klepacz R, Wysokińska-Miszczuk J. Wpływ toru oddechowego na jamę ustną [The influence of breathing mode on the oral cavity]. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2015 Dec;39(234):405-7. Polish. PMID: 26802697.
24Steffen, Patrick R et al. “The Impact of Resonance Frequency Breathing on Measures of Heart Rate Variability, Blood Pressure, and Mood.” Frontiers in public health vol. 5 222. 25 Aug. 2017, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2017.00222
25Tongue-tie (ankyloglossia). American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. http://www.entnet.org/content/tongue-tie-ankyloglossia. Accessed Feb. 13, 2018.
26Isaacson GC. Ankyloglossia (tongue-tie) in infants and children. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Feb. 14, 2018.
27Chinnadurai S, et al. Treatment of ankyloglossia for reasons other than breastfeeding: A systemic review. Pediatrics. 2015;135:e1467.
28Baker AR, et al. Surgical treatment of ankyloglossia. Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology. 2015;26:28.
29Walsh J, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of ankyloglossia in newborns and infants. JAMA Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 2017;143:1032.
30O'Shea JE, et al. Frenotomy for tongue-tie in newborn infants. Cochrane Database of Systemic Reviews. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD011065.pub2/abstract. Accessed Feb. 14, 2018.
31Davidson, J R et al. “Growth hormone and cortisol secretion in relation to sleep and wakefulness.” Journal of psychiatry & neuroscience : JPN vol. 16,2 (1991): 96-102.
32Takahashi, Y et al. “Growth hormone secretion during sleep.” The Journal of clinical investigation vol. 47,9 (1968): 2079-90. doi:10.1172/JCI105893
33Honda, Y et al. “Growth hormone secretion during nocturnal sleep in normal subjects.” The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism vol. 29,1 (1969): 20-9. doi:10.1210/jcem-29-1-20
34Morabito G, et al. (2014). Functional aerophagia in children: A frequent, atypical disorder. DOI:10.1159/000362441
35Timmons, Beverly H., and Ronald Ley. “Behavioral and Psychological Approaches to Breathing.
36https://news.stanford.edu/2020/07/21/toll-shrinking-jaws-human-health/
37Schmidt JE, Carlson CR, Usery AR, Quevedo AS. Effects of tongue position on mandibular muscle activity and heart rate function. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108:881-888
38Warren JJ, Slayton RL, Bishara SE, Levy SM, Yonezu T, Kanellis MJ. Effects of nonnutritive sucking habits on occlusal characteristics in the mixed dentition. Pediatr Dent. 2005 Nov-Dec;27(6):445-50. PMID: 16532883.
39Bishara SE, Warren JJ, Broffitt B, Levy SM. Changes in the prevalence of nonnutritive sucking patterns in the first 8 years of life. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006 Jul;130(1):31-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2004.11.033. PMI: 16849069.
40Farsi NM, Salama FS. Sucking habits in Saudi children: prevalence, contributing factors and effects on the primary dentition. Pediatr Dent. 1997 Jan-Feb;19(1):28-33. PMID: 9048410.
41Garattini G, Crozzoli P, Valsasina A. Ruolo del succhiamento protratto nell'insorgenza di alterazioni dento-scheletriche del distretto facciale: revisione della letteratura [Role of prolonged sucking in the development of dento-skeletal changes in the face. Review of the literature]. Mondo Ortod. 1990 Sep-Oct;15(5):539-50. Italian. PMID: 2280788.
42Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. Gevolgen van zuiggewoonten voor de ontwikkeling van het tandkaakstelsel [Effects of sucking habits on the dentofacial development]. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 1989 Jun;96(6):256-8. Dutch. PMID: 2635279.
43Estripeaut LE, Henriques JF, de Almeida RR. Hábito de sucção do polegar e má oclusão--apresentação de um caso clínico [Thumbsucking and malocclusion--presentation of a clinical case]. Rev Odontol Univ Sao Paulo. 1989 Apr-Jun;3(2):371-6. Portuguese. PMID: 2639459.
44Grippaudo C, Paolantonio EG, Antonini G, Saulle R, La Torre G, Deli R. Association between oral habits, mouth breathing and malocclusion. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2016 Oct;36(5):386-394. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-770. PMID: 27958599; PMCID: PMC5225794.
45Doğramacı EJ, Rossi-Fedele G. Establishing the association between nonnutritive sucking behavior and malocclusions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Dent Assoc. 2016 Dec;147(12):926-934.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2016.08.018. Epub 2016 Sep 28. PMID: 27692622.
46Lee SH, et al. How Does Open-Mouth Breathing Influence Upper Airway Anatomy? The Laryngoscope 2007; 117:1102-1106. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLG.0b013e318042aef7
47Meerman R, Brown A J. When somebody loses weight, where does the fat go? BMJ 2014; 349 :g7257 doi:10.1136/bmj.g7257
48Camacho, Macario et al. “Myofunctional Therapy to Treat Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.” Sleep vol. 38,5 669-75. 1 May. 2015, doi:10.5665/sleep.4652
49Merck Manual Professional Version. Gas-related complaints. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/gastrointestinal-disorders/symptoms-of-gi-disorders/gas-related-complaints?query=gas-related complaints#. Accessed Jan. 8, 2020.
50Chitkara DK, Bredenoord AJ, Rucker MJ, Talley NJ. Aerophagia in adults: a comparison with functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Nov 1;22(9):855-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02651.x. PMID: 16225495.
51Abraczinskas D. Overview of intestinal gas and bloating. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Jan. 8, 2020.
52https://www.healthline.com/health/aerophagia
53Proffit WR. Contemporary Orthodontics Fourth Edition. Elsevier, Health Sciences Education, Marketing.
54Guimarães KC, Drager LF, Genta PR, Marcondes BF, Lorenzi-Filho G. "Effects of oropharyngeal exercises on patients with moderate obstructive sleep apnea syndrome." Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009 May 15;179(10):962-6. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200806-981OC. Epub 2009 Feb 20. PMID: 19234106.
55de Felício, Cláudia Maria et al. “Obstructive sleep apnea: focus on myofunctional therapy.” Nature and science of sleep vol. 10 271-286. 6 Sep. 2018, doi:10.2147/NSS.S141132
56Trevisan, Maria Elaine, Jalusa Boufleur, Juliana Corrêa Soares, Carlos Jesus Pereira Haygert, Lilian Gerdi Kittel Ries, and Eliane Castilhos Rodrigues Corrêa. “Diaphragmatic amplitude and accessory inspiratory muscle activity in nasal and mouth-breathing adults: a cross-sectional study.” Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 25, no. 3 (2015): 463-468.
57Deacon, Naomi L., Rachel Jen, Yanru Li, and Atul Malhotra. “Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Prospects for personalized combined modality therapy.” Annals of the American Thoracic Society 13, no. 1 (2016): 101-108.
58Huang YS, Quo S, Berkowski JA, Guilleminault C (2015) Short Lingual Frenulum and Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children. Int J Pediatr Res 1:003
